Smart Kitchen
Flood, Smoke and Fire Hazards Protection.

The core components of any type of residential solar energy system are PV Panels to generate electricity from sunlight, Inverters that convert DC current from PV Panels into AC current applicable for household use, and Meters to monitor the power generated and consumed by household appliances. However, whether you install your system through a professional installation company, or build it yourself by purchasing DIY components, there are differences that are essential to understand for each type of system.
Grid-tied solar PV systems, also known as grid-connected systems, are the most common and foundational type of residential solar setup. These systems are directly connected to the local electricity grid, allowing homeowners to generate their own electricity while remaining connected to the utility company’s power supply. The main components of a grid-tied system include solar panels, an inverter to convert DC power from the panels to AC power for household use, and a meter that tracks energy production and consumption.
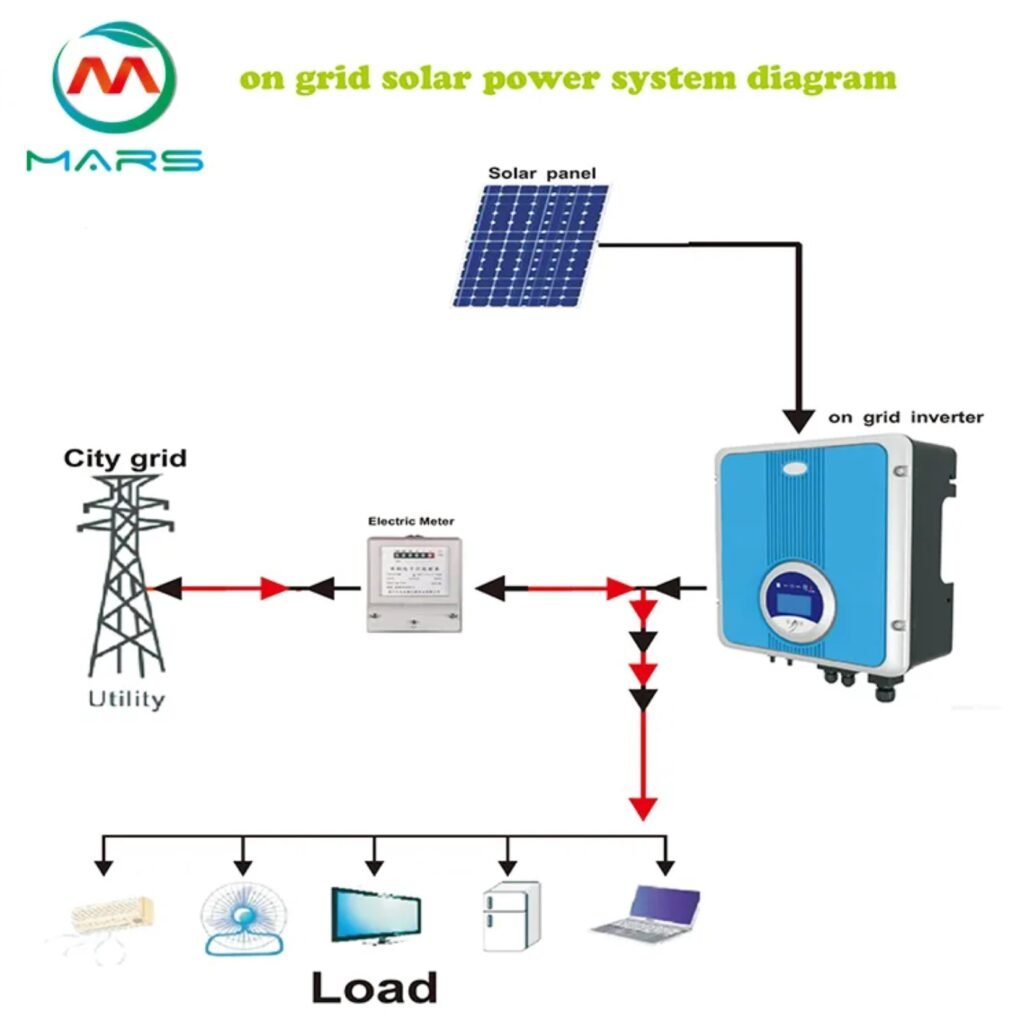
To determine the appropriate size for your home’s Grid-Tied Solar PV System, you’ll need to gather the following information: the energy consumption during daylight hours as calculated from your energy bill, the altitude and azimuth of your home’s location from Google Maps, the peak sun hours (PSH) for your area available from this website, your roof’s tilt angle, and the available roof space. To calculate the Solar PV System Size in kilowatt-hours (kWh), use the following formula:
Solar PV System Size, kWh = Daytime Energy Consumption / (% Roof Performance x PSH)
To estimate the % Roof Performance, apply the following formula:
% Roof Performance = 100% – (Your Altitude – Roof’s Tilt) / 3 + (Your Azimuth – 180) / 6
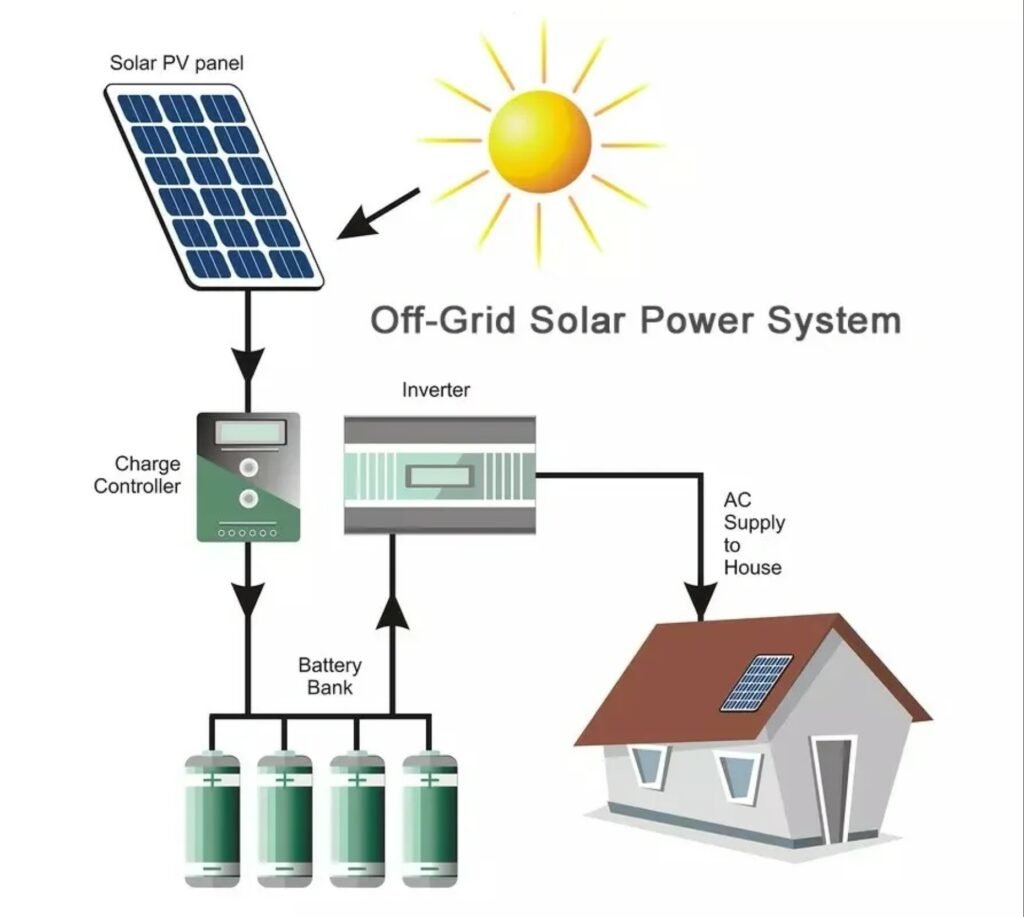
To evaluate the cost of an Off-Grid Solar PV System you have to determine the energy consumed on the property in 24 hours (Total Load), which will be required to be generated by an Off-Grid Solar PV system during peak sun hours (PSH), and the size of the Battery Bank, which has to be sufficient enough to supply energy to your home during the Days of Autonomy, when to solar energy is not available.
To calculate the Off-Grid Solar PV System Size in kilowatt-hours (kWh), use the following formula:
Solar PV System Size, kWh = Total Load / (% Eff x PSH),
where %Eff is the total efficiency of the Solar PV System, and the Total Load can be estimated using the Off-Grid Solar System Sizing Calculator.
To estimate the size of the Battery Storage, apply the following formula:
Battery Bank Size = (Total Load x Days of Autonomy) / Maximum DoD,
where DoD is the Depth of Discharge, the percentage of the battery that can be discharged without damaging it.
In the next steps, you will select a Charge Controller with a capacity enough to guarantee the longevity of the Battery Bank, the Inverter with a size exceeding the size of the Solar PV system size, and compute the number of PV Panels, considering their Power Output and Dimensions. Refer to our compilation of advanced PV Panels and their respective manufacturers.
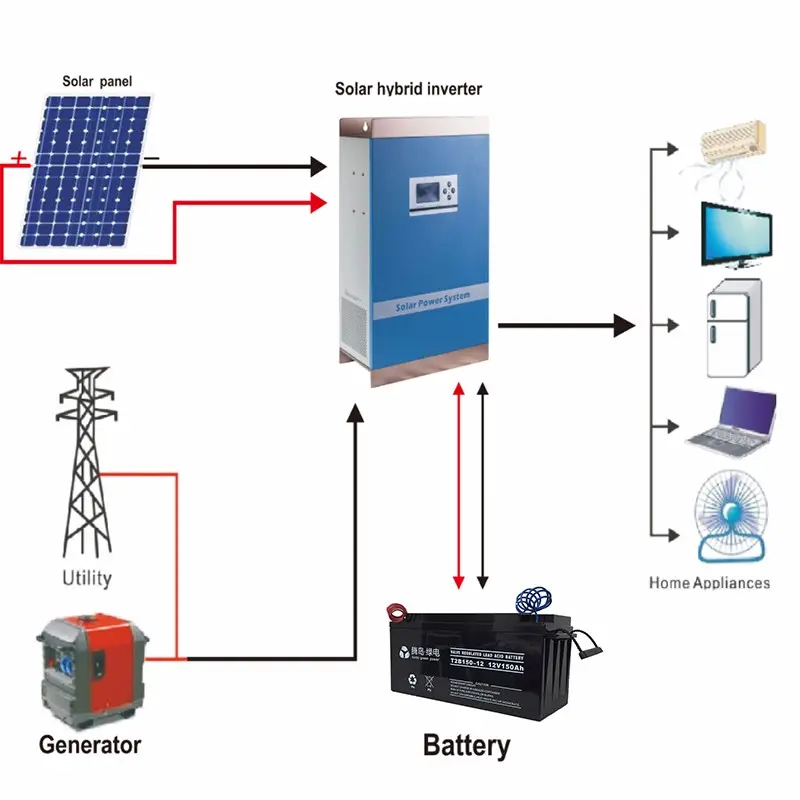
Other Solar PV Systems are taking into consideration aesthetics, and financial and space limitations. Most widely used are Community Solar PV Systems for individuals who want to benefit from solar energy but lack suitable roof space or live in rented properties, BIPV (Building-Integrated Photovoltaics) that integrates solar panels directly into a building’s architecture and offers a seamless aesthetic, and Solar Lease and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) as solutions to make solar energy accessible to a wider audience, especially those who may be deterred by the upfront costs of purchasing a solar system.
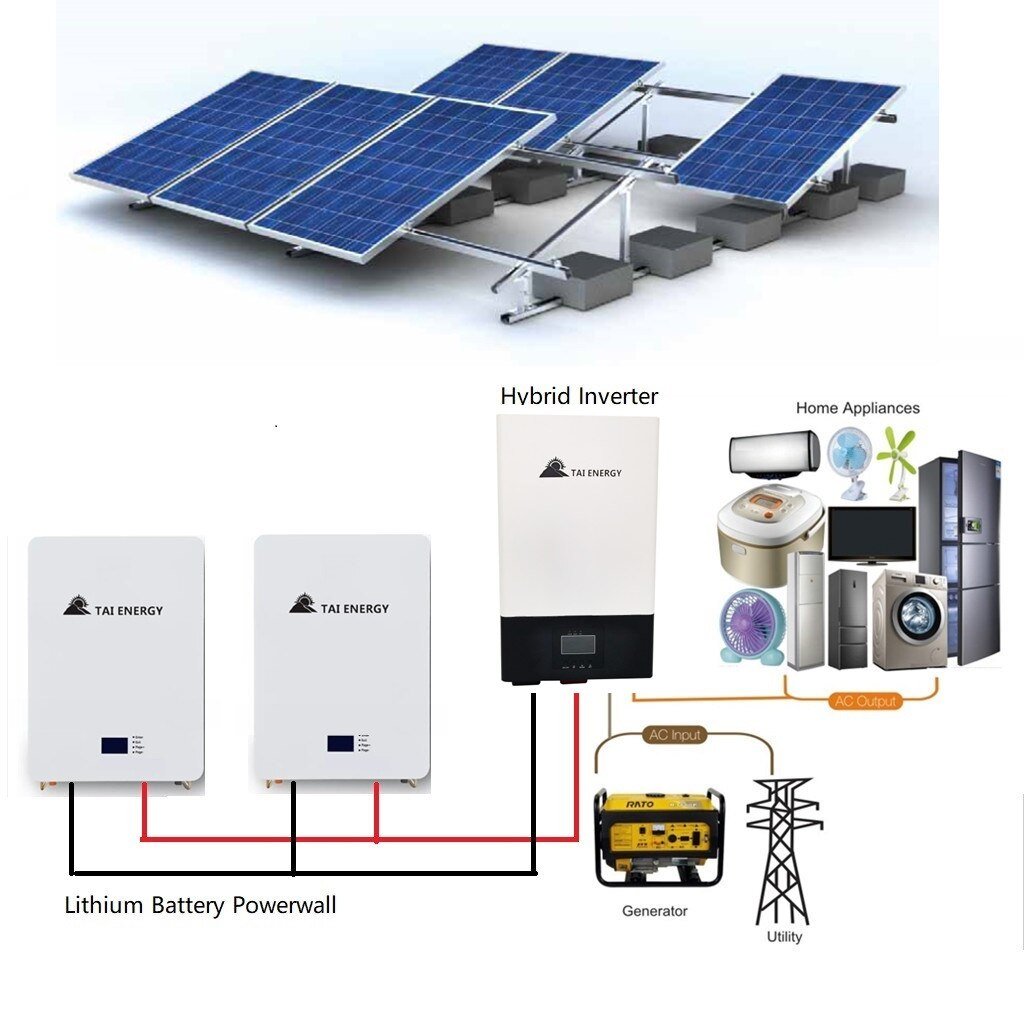
Selecting the appropriate residential solar PV system requires careful consideration of various factors, such as household energy consumption patterns, available roof space, budget, and long-term energy goals. Local regulations, incentives, and solar resource availability should be also taken into account. The choices are abundant – from grid-tied systems that offer financial incentives to off-grid solutions providing energy independence, and from hybrid systems that ensure reliability to the community and BIPV setups that promote accessibility and aesthetics.
Furthermore, the integration of Off-Grid and Hybrid Solar PV setups with Smart Home Solutions can seamlessly guarantee the continuous operation of smart home devices during power interruptions. This integration effectively optimizes power consumption from both the PV panels and the battery storage system.
If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to get in touch with us by e-mail at support@adapses.com.